🌱 What is a Vegetarian Diet?
A vegetarian diet is a lifestyle choice where individuals avoid eating meat, poultry, and seafood, but often still consume dairy and eggs depending on the variation they follow. For many, it’s not just a diet—it’s a philosophy that aligns with health, sustainability, and compassion for animals.
Globally, vegetarianism is practiced by millions of people, with especially high prevalence in countries like India, where cultural and religious traditions have embraced plant-based living for centuries.
🥕 Types of Vegetarian Diets
Not all vegetarians eat the same way. Understanding the different types can help you find what best suits your lifestyle and values:
- Lacto-Vegetarian – Includes dairy but excludes eggs, meat, poultry, and fish.
- Ovo-Vegetarian – Includes eggs but excludes dairy, meat, poultry, and fish.
- Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian – Includes both dairy and eggs but excludes meat, poultry, and fish (the most common form).
- Flexitarian (Semi-Vegetarian) – Primarily plant-based but occasionally includes meat or fish.
- Pescatarian – Excludes meat and poultry but includes fish and seafood (sometimes grouped separately from vegetarianism).
- Vegan – Excludes all animal-derived products, including dairy, eggs, honey, and gelatin.
🍏 Health Benefits of a Vegetarian Diet
Science-backed studies suggest that following a vegetarian lifestyle can lead to significant health advantages:
- Heart Health: Lower cholesterol and reduced risk of heart disease.
- Weight Management: Plant-based diets are naturally lower in calories and fat, making weight control easier.
- Diabetes Prevention: Improved insulin sensitivity and lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Digestive Health: High fiber intake promotes gut health and prevents constipation.
- Longevity: Studies link vegetarian diets with lower mortality risks.
⚖️ Nutritional Considerations
While vegetarian diets can be very healthy, there are certain nutrients to pay attention to:
- Protein: Sources include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and dairy/eggs.
- Vitamin B12: Found only in animal products—vegetarians may need fortified foods or supplements.
- Iron: Plant-based iron (non-heme iron) is less easily absorbed, but pairing it with vitamin C-rich foods helps.
- Calcium: Found in dairy, fortified plant milks, tofu, and leafy greens.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements.
🍽️ Vegetarian-Friendly Foods
Here’s a list of food groups that are typically vegetarian-safe:
- Fruits and Vegetables of all kinds
- Whole Grains: rice, oats, quinoa, wheat, barley
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas
- Dairy (for lacto-vegetarians): milk, cheese, yogurt
- Eggs (for ovo-vegetarians)
- Plant-Based Alternatives: almond milk, soy milk, vegan cheese, mock meats
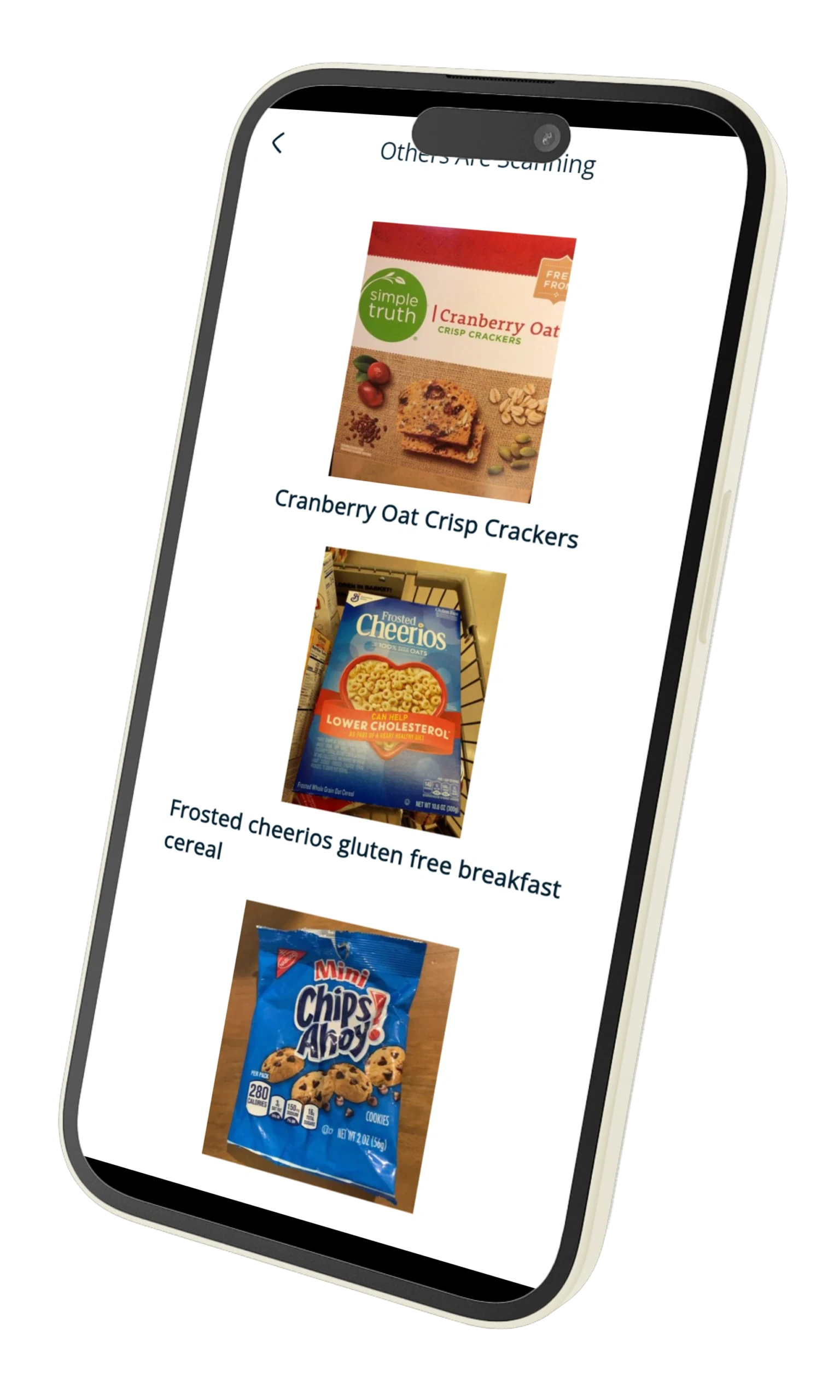
🚫 Common Hidden Animal Ingredients
Vegetarians often encounter challenges when packaged foods contain hidden animal-derived ingredients. Here are some to watch out for:
- Gelatin: Found in candies, marshmallows, capsules.
- Rennet: Enzyme from animal stomachs used in cheese production.
- Lard: Used in baked goods, tortillas, or pastries.
- Fish Sauce: Common in Asian cuisine.
- Whey/Casein: Dairy by-products found in protein powders and processed foods.
🌍 Cultural and Religious Perspectives
Vegetarianism is deeply tied to cultural and religious traditions:
- Hinduism: Promotes vegetarianism as part of ahimsa (non-violence).
- Buddhism: Many Buddhists follow a vegetarian diet for compassion.
- Jainism: Strictly vegetarian, with avoidance of root vegetables.
- Western Trends: Increasing adoption due to health, ethics, and environmental awareness.
🌐 Environmental Impact of Vegetarian Diets
Switching to a vegetarian diet contributes positively to the planet:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to meat-heavy diets.
- Requires less land, water, and resources.
- Encourages biodiversity by lowering demand for livestock farming.
📊 Vegetarian Diet Trends
According to research:
- 10% of the global population identifies as vegetarian or plant-forward.
- Plant-based food sales are growing by over 10% annually.
- Gen Z and Millennials are driving much of this growth due to sustainability concerns.
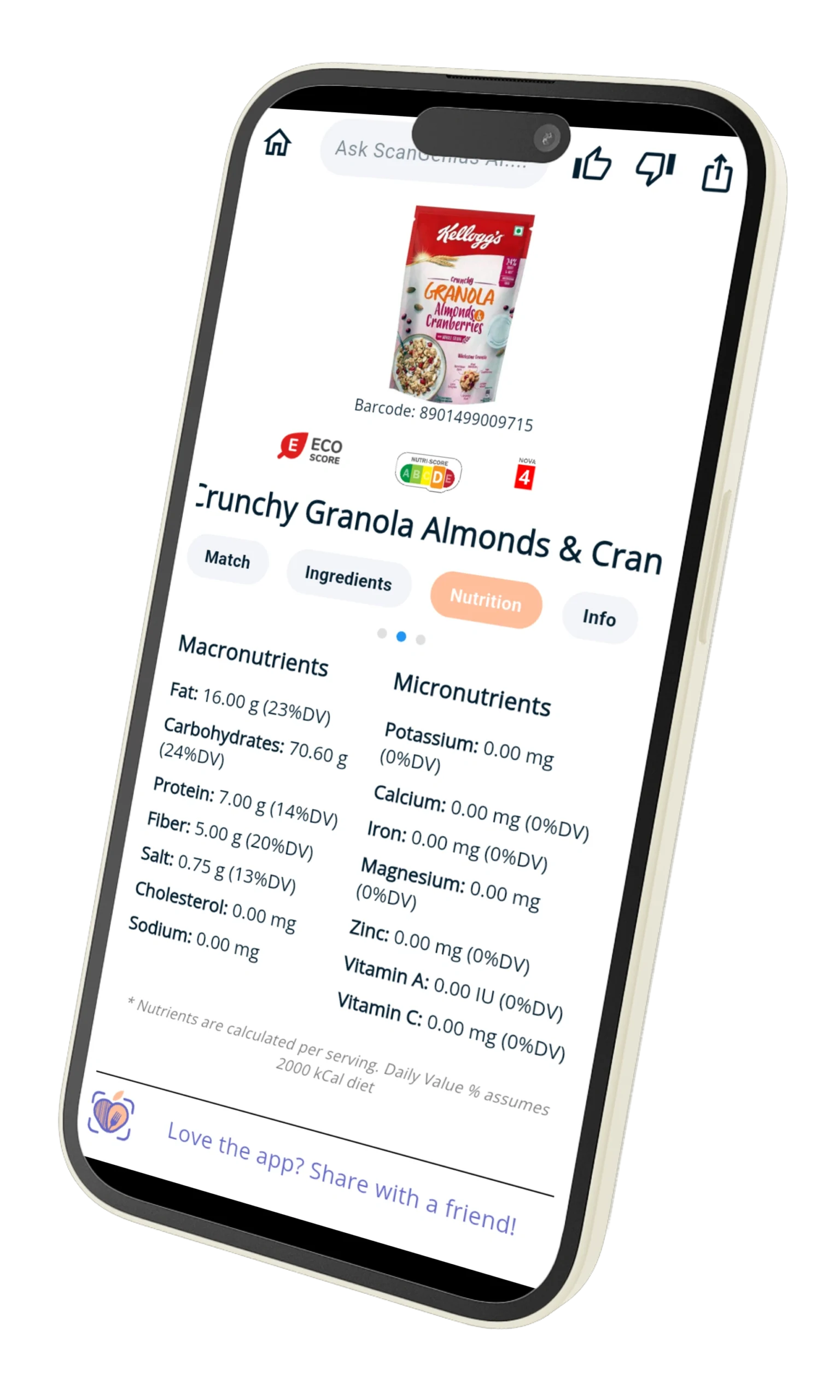
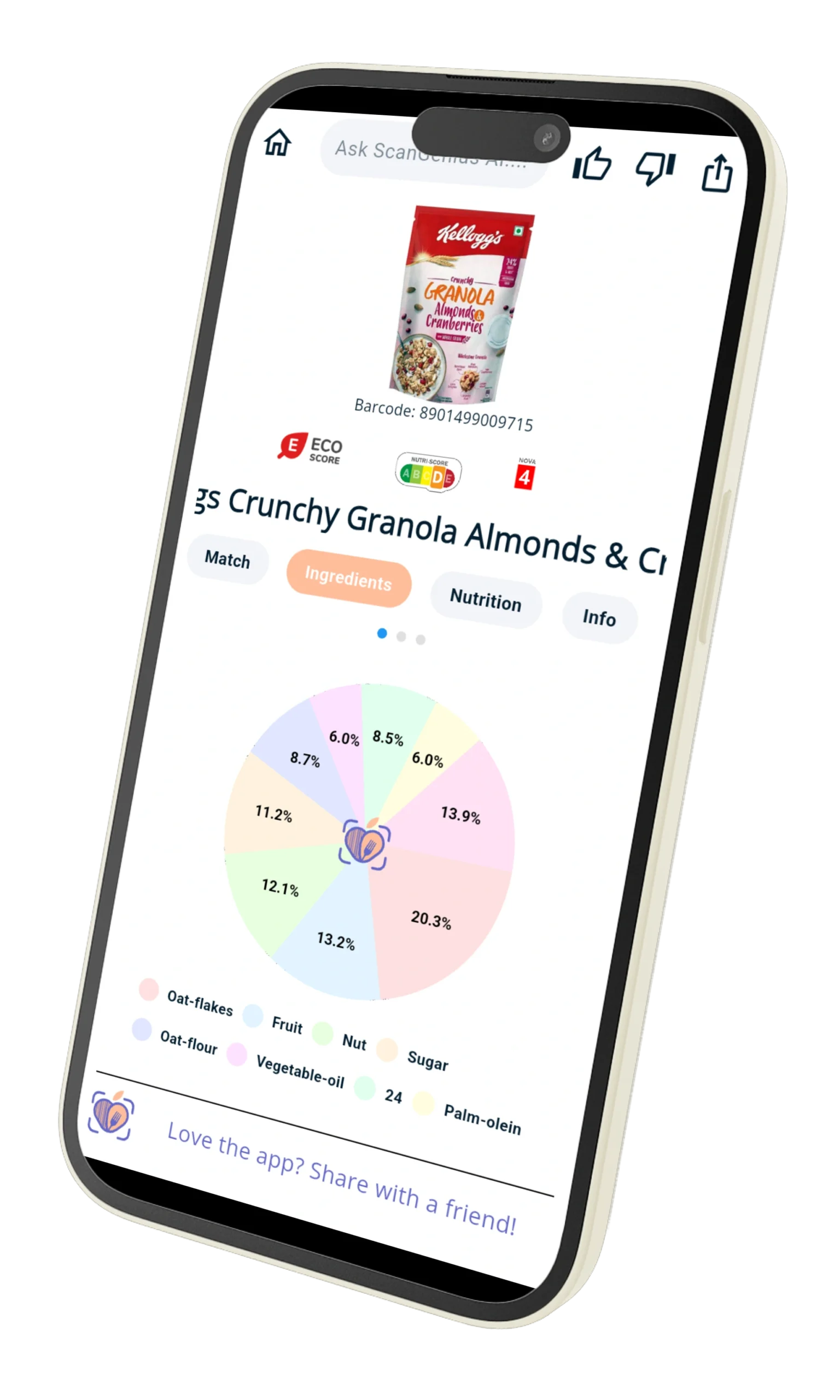
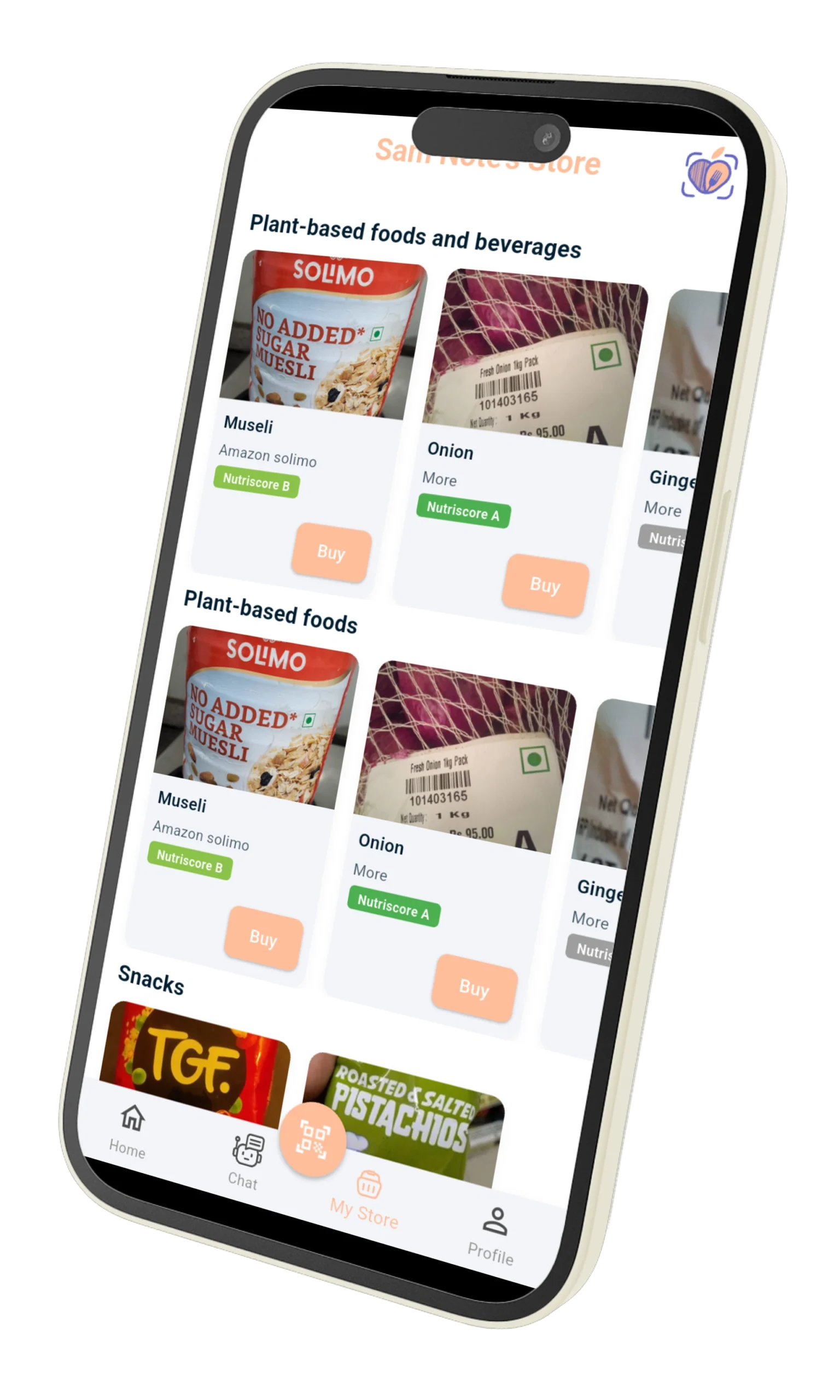
🤖 How Food Scan Genius Helps Vegetarians
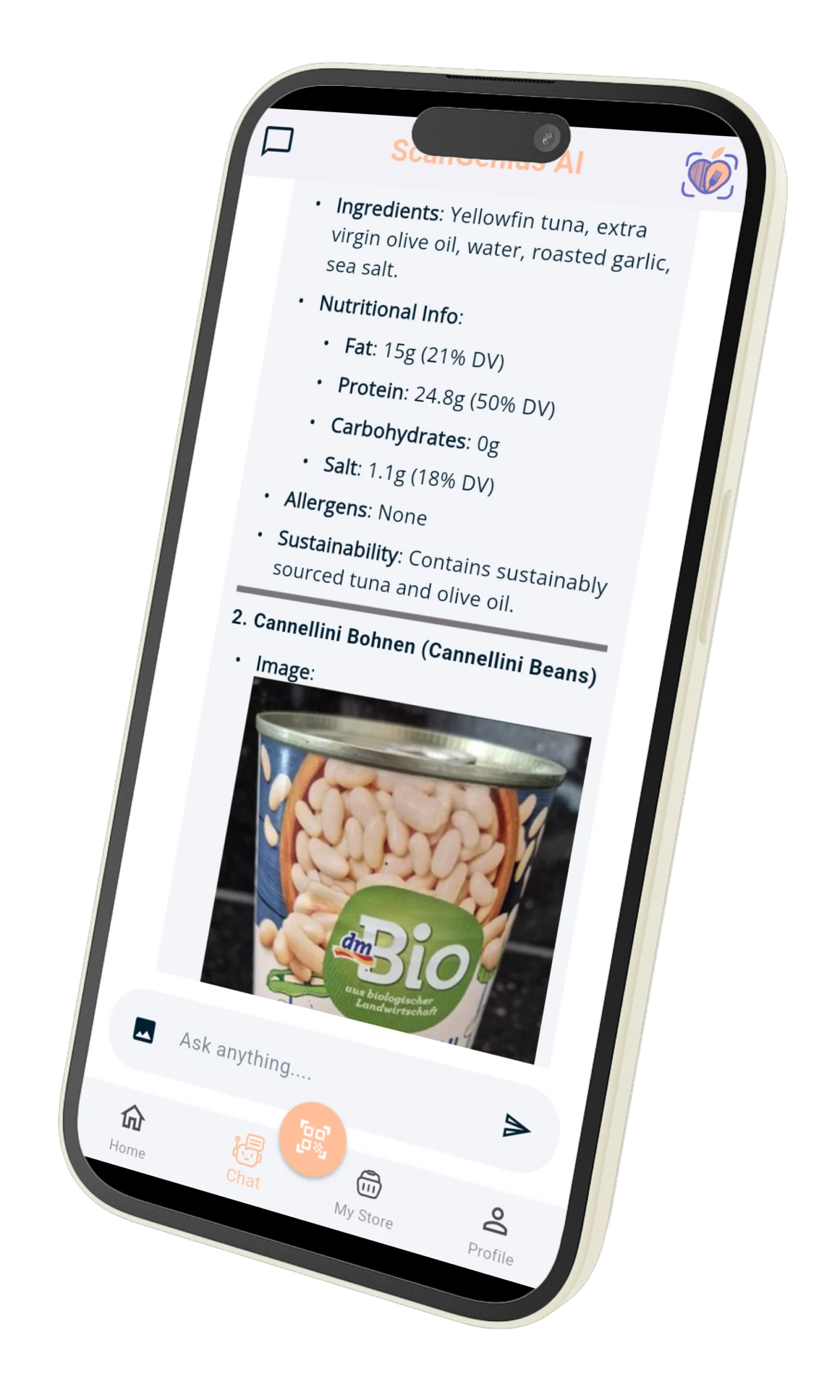
Food Scan Genius uses AI-driven ingredient scanning to help vegetarians avoid hidden animal ingredients and discover safe, delicious alternatives. With our app, you can:
- Scan any packaged food to check for vegetarian suitability.
- Identify hidden animal ingredients instantly.
- Discover plant-based alternatives that match your taste preferences.
- Filter grocery lists and recipes according to your vegetarian type.
✅ Practical Tips for Thriving as a Vegetarian
- Plan meals ahead to ensure balanced nutrition.
- Stock up on protein-rich staples like lentils, beans, tofu, and nuts.
- Read labels carefully or use Food Scan Genius to avoid hidden ingredients.
- Experiment with global cuisines—Indian, Mediterranean, and Middle Eastern diets are rich in vegetarian options.
- Stay flexible and explore fortified foods to meet nutrient needs.
🔑 Key Takeaways
- Vegetarian diets are diverse—choose the type that suits your health, culture, and ethics.
- Health benefits include better heart health, weight management, and longevity.
- Watch out for hidden animal ingredients in packaged foods.
- Vegetarian living is both a personal and global movement for health, sustainability, and compassion.
- AI-powered tools like Food Scan Genius make the transition easier and smarter.
📢 Final Word
Whether you’re new to vegetarianism or a lifelong plant-based eater, making informed food choices is key to staying healthy and aligned with your values. With Food Scan Genius, you can confidently navigate food labels, enjoy diverse cuisines, and embrace a sustainable, ethical, and nourishing lifestyle.